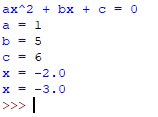In this post I would be writing a guide on how to make a quadratic equation solver where you input a,b and c into the equation:

Plan
- Inputs
- Solve the equation
Maths
First we need to understand how we are going to solve an quadratic equation. I used the quadratic equation. I also made my code print no real solutions when the discriminant is less than 0.
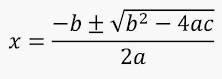

Inputs
print('ax^2 + bx + c = 0')
A=int(input('a = '))
B=int(input('b = '))
C=int(input('c = '))
print(‘ax^2 + bx + c = 0’)
This is to tell the user what a,b and c represent.
Solve the equation
Discriminant=math.sqrt((B*B)-(4*A*C))
if Discriminant<(0):
print('No real values')
else:
print('x = '+str( ((0-B)+Discriminant)/(2*A) ))
print('x = '+str( ((0-B)-Discriminant)/(2*A) ))
Discriminant=math.sqrt((BB)-(4A*C))
I had to use the math module to do “math.sqrt()”. I did import math at the top of my code.
if Discriminant<(0):
print(‘No real values’)
This checks if the values have a solution
((0-B)+Discriminant)/(2*A)
((0-B)-Discriminant)/(2*A)
This subs the values into the quadratic equation.
The full code
#imports
import math
#Inputs
print('ax^2 + bx + c = 0')
A=int(input('a = '))
B=int(input('b = '))
C=int(input('c = '))
#Solve the equation
Discriminant=math.sqrt((B*B)-(4*A*C))
if Discriminant<(0):
print('No real values')
else:
print('x = '+str( ((0-B)+Discriminant)/(2*A) ))
print('x = '+str( ((0-B)-Discriminant)/(2*A) ))